2 Introduction and Survey
Risks and Side Effects and/or Discomforts. A script is a keyword selection. It is characterized by my ideas and prejudices about electronics and circuit design strongly but not completely. And as common, this script has been written with a lot of time constraints, hence, it is not fully proof read and contains errors. Therefore, you should never rely solely on this script. Consult other sources like books, papers and application notes, also.
2.1 Learning outcomes
The objective of this module is a project course in which students possess a thorough understanding of basic principles, challenges and limitations in microelectronic circuit design through a design project. After completion of this module students …
- Knowledge and understanding (extension, consolidation and understanding of knowledge)
- … have worked in project teams to generate a database that can (potentially) be sent out for fabrication,
- … have become familiar with microelectronic circuit design;
- Using, applying and generating knowledge (applying and transferring knowledge, Scientific innovation)
- … will have basic intuition by studying a selection of commonly used circuit and design techniques,
- … will be prepared for further study of mixed-technology systems;
- Communication and cooperation
- … do circuit development and design in a team,
- … decide autonomous about organization and conduct of design steps,
- … present progress and results to supervisors and peers,
- … assess results from experiments, evaluate and analyze in a team and document scientifically,
- Reflection of academic and professional identity
- … reflect system design and test setup with regard to alternative designs,
- … adhere to standards of professional action and documentation.
2.2 Analysis vs. Design
Unlike common perception, analog circuit analysis and design is not “black magic” Circuit analysis. * The art of decomposing a circuit into manageable pieces. * Based on the simple, but sufficiently accurate models. * “Just-in-time” modeling – Do not use a complex model unless you know why it’s needed!
- One circuit \(\Rightarrow\) one solution
Circuit design.
- The art of synthesizing circuits based on experience from extensive analysis
- One set of specifications \(\Rightarrow\) Many solutions
- Design skills are best acquired through learning by doing
- This is why we’ll have a design project.
2.3 Signal Conditioning
Wikipedia. “In electronics, signal conditioning means manipulating an analog signal in such a way that it meets the requirements of the next stage for further processing.”
“Signal conditioning can include amplification, filtering, converting, range matching, isolation and any other processes required to make sensor output suitable for processing after conditioning.”
2.4 Design Project
Design and Characterization of an Analog Universal Filter (Biquad).
- Basics of filter design
- Approximation and filter template
- Biquads
- Behavioural and macro modelling
- Filter design
- Signals and systems analysis
- Circuit design and layout
- Opamps
- Integrators
- Adders
- ASLK Pro and Red Pitaya STEMlab
- Experiment 4 – Design of Analog Filters
- Measurements: Steady State and Frequency Response
- Simulation with ngspice (KiCAD/Xschem)
- Data readout and management with Matlab and/or Python
- Behavioural modelling with Matlab and/or Python
2.5 Scientific Computing
2.6 EDA Tools
- PCB / System Design
- IC / Silicon Design
2.7 OS-Tools
2.8 Code Editors
2.9 Data Science
2.10 Publish Computational Content
2.11 Are you writing or TeXing?
2.12 LaTeX Editors
- IDE’s
- Collaborative Frameworks
2.13 Bibliography and LaTeX
2.14 Design Project Flow
- Literature research in journals, professional (serious) internet forums (e.g. application notes of semiconductor companies) and library
- Set-up literature database
- Concept of your system
- Partitioning
- Functions
- Work packages
- Design, implementation and validation
- Mathmatical description
- SPICE modeling and simulation
- Data analysis and validation
- Design report
2.15 Assignments
Design Project. * System Modell Matlab/Python * Circuit Design SPICE * Characterisation/Measurement Red Pitaya * Technical/Design Report
2.16 Course Prerequisites
- Fundamentals of linux operating systems
- Fundamentals of microelectronics
- Device physics and models
- Transistor level analog circuits, elementary gain stages
- Control theory (requency response, feedback, stability)
- System theory (Laplace and Z-transform)
- Prior exposure to SPICE, Matlab/Simulink, Python (NumPy, SciPy) or equivalent
- Please talk to me if you are not sure if you have the required background
2.17 Course Topics
- Design of Operational Transconductance Ampilfiers (OTAs)
- Analysis and design
- OTAs as integrators
- Noise analysis
- Continuous time filters
- Biquad designs
- Approximation errors
- Circuit simulation
- Switched capacitor filters
- Sampling
- Bilinear transform s-domain to z-domain
2.18 Brave New World

2.19 From Sand to Silicon (Infineon, Dresden)
2.20 Sand to Silicon (GlobalFoundries, Desden)
2.21 FinFET (Intel)
2.22 TSMC Fab (Next Gen 7/5 nm)
2.23 Once upon a time …
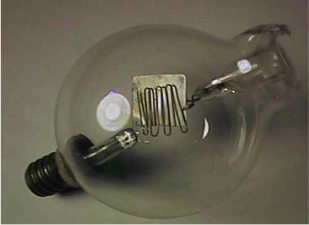

2.24 First IC and today’s chips

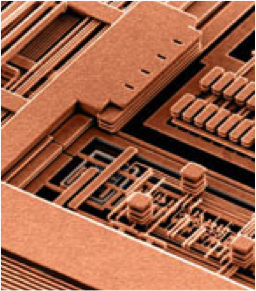
2.25 Packaging Densities
